|
The iPhone Wiki is no longer updated. Visit this article on The Apple Wiki for current information. |
Difference between revisions of "/System/Library/CoreServices/SpringBoard.app"
m |
Musicguy32 (talk | contribs) (→Files: please fix formatting, I am new here, and am aware of how horrendous it looks.) |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[ |
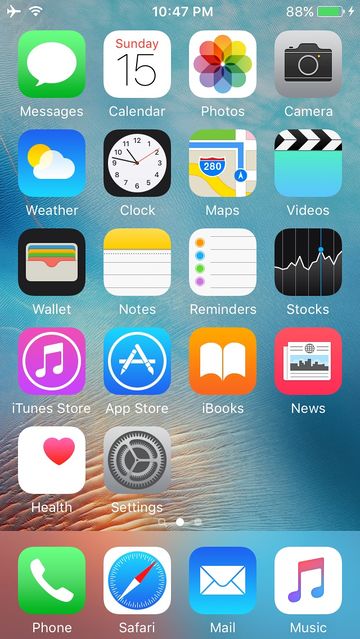
+ | [[File:IOS4.jpg|right|thumb|360px|SpringBoard on an unmodified [[N42AP|iPhone 5]] running [[iOS]] 9.3.1]] |
__NOTOC__ |
__NOTOC__ |
||
== Summary == |
== Summary == |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
* SpringBoard is responsible for most of the interactions with CoreTelephony |
* SpringBoard is responsible for most of the interactions with CoreTelephony |
||
| + | Starting in iOS 6, some of SpringBoard's former functions are now in [[backboardd]]. |
||
| − | === MobileSubstrate Extensions === |
||
| + | |||
| − | After jailbreaking the device, SpringBoard.app can be extended with 3rd party extensions injected by [[Mobile Substrate]]. |
||
| + | === Cydia Substrate Extensions === |
||
| + | After jailbreaking the device, SpringBoard.app can be extended with 3rd party extensions injected by [[Cydia Substrate]]. |
||
| + | |||
=== Alternatives === |
=== Alternatives === |
||
| − | + | While there are no publicly available fully-fledged SpringBoard alternatives, iOS devices are briefly flashed with [[Internal Firmware]] during the manufacturing process that is used for testing purposes. It includes [[SwitchBoard.app]], a simple launcher for other internal utilities, such as [[SkankPhone]] and [[BurnIn]]. |
|
==Main Application Ports== |
==Main Application Ports== |
||
| Line 27: | Line 30: | ||
*Related artwork |
*Related artwork |
||
*ring.m4r (Marimba) |
*ring.m4r (Marimba) |
||
| + | *<a href = “ https://www.theiphonewiki.com/wiki//private/var/mobile/Library/Preferences/com.apple.springboard.plist”>com.Apple.springboard.plist</a> |
||
== Parents == |
== Parents == |
||
| − | + | {{parent|System|Library|CoreServices}} |
|
[[Category:Filesystem]] |
[[Category:Filesystem]] |
||
Latest revision as of 21:01, 11 March 2021
Summary
SpringBoard.app is essentially iOS's graphical user interface (much the same as GNOME is to Linux, Explorer is to Microsoft Windows, and Finder is to Mac OS) and manages graphical services ranging from icon badges, the dock, multitasking, and folders (among others). When it is launched, it registers PurpleSystemEventPort, essentially making it the main application.
Primary Functions
- SpringBoard acts a stacking window manager, rendering the child applications
- SpringBoard activates/deactivates and manages memory of the UIKit applications it launches
- SpringBoard is responsible for most of the interactions with CoreTelephony
Starting in iOS 6, some of SpringBoard's former functions are now in backboardd.
Cydia Substrate Extensions
After jailbreaking the device, SpringBoard.app can be extended with 3rd party extensions injected by Cydia Substrate.
Alternatives
While there are no publicly available fully-fledged SpringBoard alternatives, iOS devices are briefly flashed with Internal Firmware during the manufacturing process that is used for testing purposes. It includes SwitchBoard.app, a simple launcher for other internal utilities, such as SkankPhone and BurnIn.
Main Application Ports
- com.apple.SpringBoard
- com.apple.SpringBoard.UIKit.migserver
- PurpleSystemEventPort
- CARenderServer
Children
Folders
- Translations
Files
- Model definition file(s)
- Related artwork
- ring.m4r (Marimba)
- <a href = “ https://www.theiphonewiki.com/wiki//private/var/mobile/Library/Preferences/com.apple.springboard.plist”>com.Apple.springboard.plist</a>